CORONA Insights: 2021: Promising Outpatient Treatments (February 2022)
As data from randomized controlled trials continues to emerge, the CORONA Project has identified several therapies shown to be safe and effective in both outpatient and inpatient settings. The available data, as seen in the STORM Viewer have shown that timing of therapeutics is crucial, with monoclonal antibodies and antivirals more efficacious early in disease course, and steroids and immunomodulators best used later, in more severe cases. Here, several of the key therapeutics used early, in an outpatient setting, are reviewed.
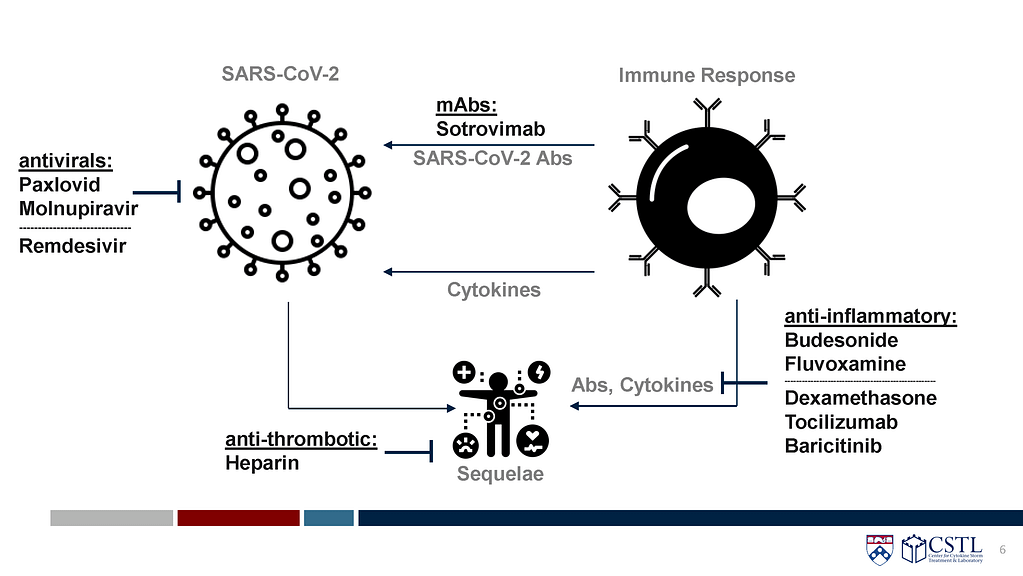
Sotrovimab
- Sotrovimab is a monocloncal antibody against highly conserved region of spike. It is delivered intravenously.
- An outpatient RCT (N=583) in adults with mild to moderate COVID-19 at high risk for severe illness (>55 years old or at least one risk factor) found a relative risk reduction of hospitalization or death of 85% (p=0.002).
- An inpatient RCT (N=182) did not demonstrate benefit.
- Availability is limited.
- CORONA Grades:
- Outpatient: Grade A
- Inpatient: Grade B/C
Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir)
- Paxlovid is an antiviral that inhibits viral replication by inhibiting the main protease needed for replication.
- It is taken orally twice a day for 5 days by high-risk patients early in disease course.
- A large RCT (n= 2,246) in non-hospitalized, high-risk adults with COVID-19 showed a reduced risk of hospitalization or death by Day 28 of 89%.
- Paxlovid: 5/697 (0.7%) hospitalized with no deaths.
- Placebo: 44/682 (6.5% ) hospitalized with 9 subsequent deaths.
- CORONA Grades:
- Outpatient: Research Prioritization Grade B
- Inpatient: N/A
Molnupiravir
- Molnupiravir is an antiviral that increases frequency of viral RNA mutations, impairing SARS-CoV-2 replication. It is taken orally twice a day for 5 days.
- A large RCT (N=1408) in adults with mild to moderate COVID-19 showed a reduction in hospitalization or death from 9.7% to 6.8% (30% reduction).
- CORONA Grades:
- Outpatient: Research Prioritization Grade A
- Inpatient: N/A
Remdesivir
- Remdesivir is an antiviral that inhibits SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. It is given intravenously daily for 3 days.
- A large RCT (N=562) evaluated non-hospitalized adults with confirmed COVID-19 plus at least one risk factor. It showed that the risk of hospitalization or death by day 28 was lowered (relative risk reduction: 87%).
- Remdesivir: 2/279 (0.7%) were hospitalized or died by Day 28 for COVID-19-related cause
- Placebo: 15/377 (5.3%) were hospitalized or died by Day 28 for COVID-19-related cause
Note: Hospitalization or death by all cause had a relative risk reduction of 72%
- CORONA Grades:
- Outpatient: Research Prioritization Grade A
- Inpatient: Research Prioritization Grade
Budesonide
- Budesonide is an inhaled corticosteroid (anti-inflammatory drug)
- A small RCT (N=139) showed reduced likelihood of urgent care and time to recovery
- A large outpatient RCT (N=1856) of high-risk patients revealed significant reduction in time to recovery (11.8 vs. 14.7 days) and a reduction in hospitalization or death of 25% (6.8% vs 8.8%)
- CORONA Grades:
- Outpatient: Grade A
- Inpatient: N/A
Fluvoxamine
- Fluvoxamine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor with potential anti-inflammatory and antiviral effects
- A small RCT (N=152) reduced clinical deterioration efficacy (0/80 vs 6/72)
- A large RCT (N=1497) reduced risk of ED visit or hospitalization by 32%
- CORONA Grades:
- Outpatient: Grade A
- Inpatient: N/A
Summary
To date, at least 6 promising therapies have been identified by The CORONA Project for treating COVID-19 early in high-risk populations. However, limitations exist for several several drugs. Sotrovimab and Paxlovid have severely limited supplies available to patients, while remdesivir must be given intravenously in a clinic setting, limiting patient access. Others, including generic drugs like budesonide and fluvoxamine, have received little attention compared to novel therapies and may be underutilized in patients who may benefit from early treatment. As COVID-19 cases continue to spread and deaths, possibly preventable, continue to occur, the CORONA Project’s analysis of emerging data continues in pursuit of additional promising therapies.
| Risk of hospitalization: |
| Sotrovimab (IV mAb): 1 RCT, relative risk reduction of 85% (high-risk population) |
| Paxlovid (oral antiviral): 1 RCT, relative risk reduction of 89% (high-risk population) |
| Molnupiravir (oral antiviral): 1 RCT, relative risk reduction of 30% (high-risk population) |
| Remdesivir (IV antiviral): 1 RCT, relative risk reduction of 87% (moderate risk population) |
| Budesonide (inhaled steroid): 2 RCTs, large trial reported 25% risk reduction (high-risk population) |
| Fluvoxamine (oral SSRI): 2 RCTs, large trial reported relative risk reduction of 32% (moderate risk pop) |
Read additional articles about the CORONA Project and its findings in our CORONA INSIGHTS blog.
Disclaimer:
CORONA Insights and the CORONA Treatment Registry are for informational and exploratory purposes only and are not intended to be used as medical advice. This site is intended to facilitate the exploration of therapies mentioned in COVID-19 medical literature. Users assume full responsibility for use of the information on this site and understand and agree that the CDCN and its third party content providers are not responsible or liable for any claim, loss, or damage (including personal injury or wrongful death) resulting from its use. Reliance on any information provided by the CDCN or third party content providers is solely at your own risk. Our extractors do not assess the scientific merits of these results and conclusions. We disclaim any warranty concerning the accuracy, timelessness, and completeness of information on this site. This site also contains links to external sites. The CDCN is not responsible for the content and does not make any representations regarding their content, timeliness, or accuracy.